
Frankfurter idea 1: Establish the Buchmesse. Dalmatian idea 4: Center of Art and Literature. Brazilian idea 2: Research of John of Nassau. Brunswicker idea 6: Leibnitz and Lessing. West Indies idea 2: Blue Mountain Coffee. Please help with verifying or updating this table. Especially Colonialism is notorious for late spawning due to having only a 5% chance to spawn in a province, which effect is increased if there are not many colonizers or the colonizers have few coastal centers of trade or developed provinces connected to their capital. If none or only a few provinces are eligible for spawning, it can take years or even decades for an institution to show up. If only 3 provinces can get it to spawn for an institution with a 10% spawn chance there is a 90% × 90% × 90% = 72.9% chance that it won't spawn in the beginning of that year. Each eligible province for an institution has a fixed chance (5% to 25% depending on the institution) to get it to spawn in that province. There are a total of 8 different institutions that appear throughout the game (except for the first which is present at the beginning of the game in 1444), at roughly 50-year intervals starting in 1450 and ending in 1750.Įach year all provinces an institution can spawn in are randomly given a chance to spawn the institution. Embracing an institution requires that institution to be fully present in provinces containing at least 10% of a country's development (modified by local autonomy), after which it requires an amount of ducats dependent on the remaining development in provinces where the institution is not fully present. The first tech of an institution receives an institution penalty of +15% the next one +30% and all following techs +50%, this modifier can stack if multiple requirements are unfullfilled. Technologies require specific Institutions to be embraced and will have increased tech cost penalties otherwise (as shown through the icons above the technology, where those shown in red or grayed out are increasing the cost). Institutions are fundamental advances in civilization and are the primary determinant of technology cost. In this way each category got certain duties to perform and people of every type existed in the European feudal system.Please help with verifying or updating older sections of this article.Īt least some were last verified for version 1.31. In return of land they were either required to serve the knight or pay rent for the land. The responsibility of peasants was to farm the land and provide food supplies to the whole kingdom. PeasantsĪfter knights came the lowest category or class of people in the feudal system – the peasants. The king’s fighting strength always depended on the good supply of trained knights. The under tenants were homage to his lord, just as the lord has done to the king. They also gave some parts of their land to peasants for services, and in this way they became able to support and sustain themselves. Knights were the fighters in the war, and were also known as under tenants as per the European feudal hierarchy. 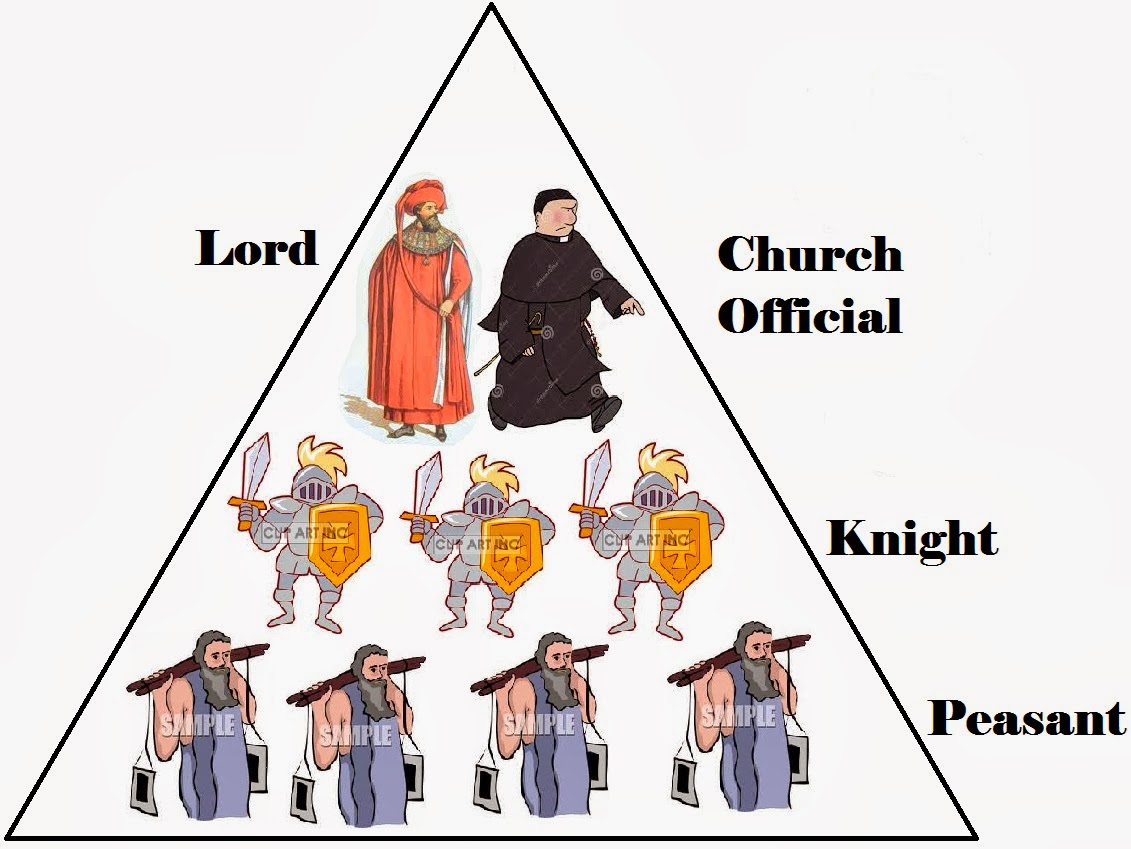
They subletted their lands to knights in return for the military services. To arrange knights for the war, bishops and barons did the same as the king.

The kings required these tenants in chiefs to be always ready to fight for the king, and were also expected to bring along certain number of knights depending on the size of the war. They were required to take oath that they will serve the kingdom and the king faithfully and will perform their due services throughout their life. The tenants in chief were required to perform certain ceremonies of homage, before king could handover the land to them. These were known as tenant-in chief who used to get land from the king himself. King kept about a quarter of his royal estates for his personal usage and divided the rest of the kingdom among his noble men – Barons and Bishops. KingĪll the land in the kingdom belonged to king and hence king was on the top of the hierarchical structure. Every higher level in the hierarchy had greater privileges, power and land than the lower class following them. The feudal system hierarchy was divided into four categories, where each category used to represent a certain class of people. Under the feudal system all the people were divided in a well-defined structure where every category or the class of people had certain duties to perform, and in return they were rewarded with land. As a result of this joint venture the European feudal system came into being.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
